cPanel & WHM® has introduced a revolutionary new way to manage WordPress sites. The WP Toolkit (WPTK) empowers web hosting providers and site owners to install, secure, and configure multiple websites in a single easy-to-use interface. This Toolkit simplifies site management by automating complex tasks and providing a unified configuration and support experience.
Before the WP Toolkit, WordPress Manager was cPanel’s primary WordPress interface. However, while it surfaces useful configuration and backup settings, users often found themselves turning to site admin pages or command-line tools like WP-CLI. In contrast, the WP Toolkit offers a collection of tools that provide a complete WordPress management solution.
In this article, we’ll highlight some of the features that make cPanel & WHM and WPTK the ideal platform for WordPress hosting providers, including:
- Managing WordPress Plugins and themes
- Cloning WordPress sites and creating staging sites
- One-click WordPress security hardening
- Smart updates
- Multi-Site Automatic updates
Installing WordPress, Themes, and Plugins
WordPress Manager offered a straightforward site installation with a handful of configuration options. WP Toolkit is significantly more flexible and configurable.
Deploying New WordPress Sites
cPanel users can configure and automatically install sites with customized plugin and theme sets, making the usually time-consuming task of plugin and theme installation almost instantaneous.

The Toolkit comes with several sets, such as WordPress Essentials, WordPress Classic, and the Ecommerce Pack. However, the real power lies in custom sets created in WHM and made available to cPanel users. This feature allows web hosts and server administrators to provide a single-click deployment process that includes everything users need to get started with a new site.
The site installation tool also allows users to pre-select automatic update settings before installation. They can choose any combination of automated update strategies for major and minor releases of WordPress, plugins, and themes.
Managing Plugins and Themes
With WP Toolkit, cPanel users can browse, install, and activate plugins and themes from within cPanel. Unlike WordPress Manager, WPTK offers both single and multi-site management tools. If you’ve ever wanted to activate, deactivate, install, uninstall, or update a plugin on dozens of sites at the same time, you’re going to love WP Toolkit.
Cloning WordPress Sites and Creating Staging Sites
One of the Toolkit’s killer features is cloning, which creates an identical copy of a site. It can clone any site hosted on your server in seconds, making the clone available at a new subdomain, which it creates automatically, or at an existing domain or subdomain.

Site cloning has many uses, but the primary purpose is to deploy staging and testing sites based on users’ production sites. What was once a complex process requiring third-party plugins or laborious manual database and file copying is now entirely automated.
In addition to cloning, the Toolkit includes a data copying feature that transfers files and database tables between sites. Users can copy files, the database, or both, with fine-grained control over which tables they would like to include or exclude.
One-Click WordPress Security Hardening
A typical WordPress installation starts with WordPress core, followed by plugins and themes, and then an involved security hardening process to remove potential vulnerabilities. We’ve already seen how the Toolkit automates the installation, and you’ll be happy to hear that it takes care of security hardening as well.
The WPTK has two security hardening features. First, it applies critical fixes during installation, ensuring WordPress is secure the moment it goes online.

Second, it scans sites for non-critical risks, displaying issues in an interface that users browse to activate (or revert) fixes. As you might be expecting, hardening can be applied site-by-site or to many sites simultaneously, allowing web hosts to harden hundreds of sites in a couple of clicks.
If you want to know more about security hardening with the WP Toolkit and the vulnerabilities it can fix, read WordPress® Hardening: One-Click Security with cPanel
Smart Update
Smart Update is an exciting feature enabled by the Toolkit’s ability to clone WordPress sites. Have you ever updated to a new version of a plugin or theme, only to find that a bug or incompatibility breaks your site? It’s one reason users avoid updating, exposing WordPress to security risks that can result in compromised sites.
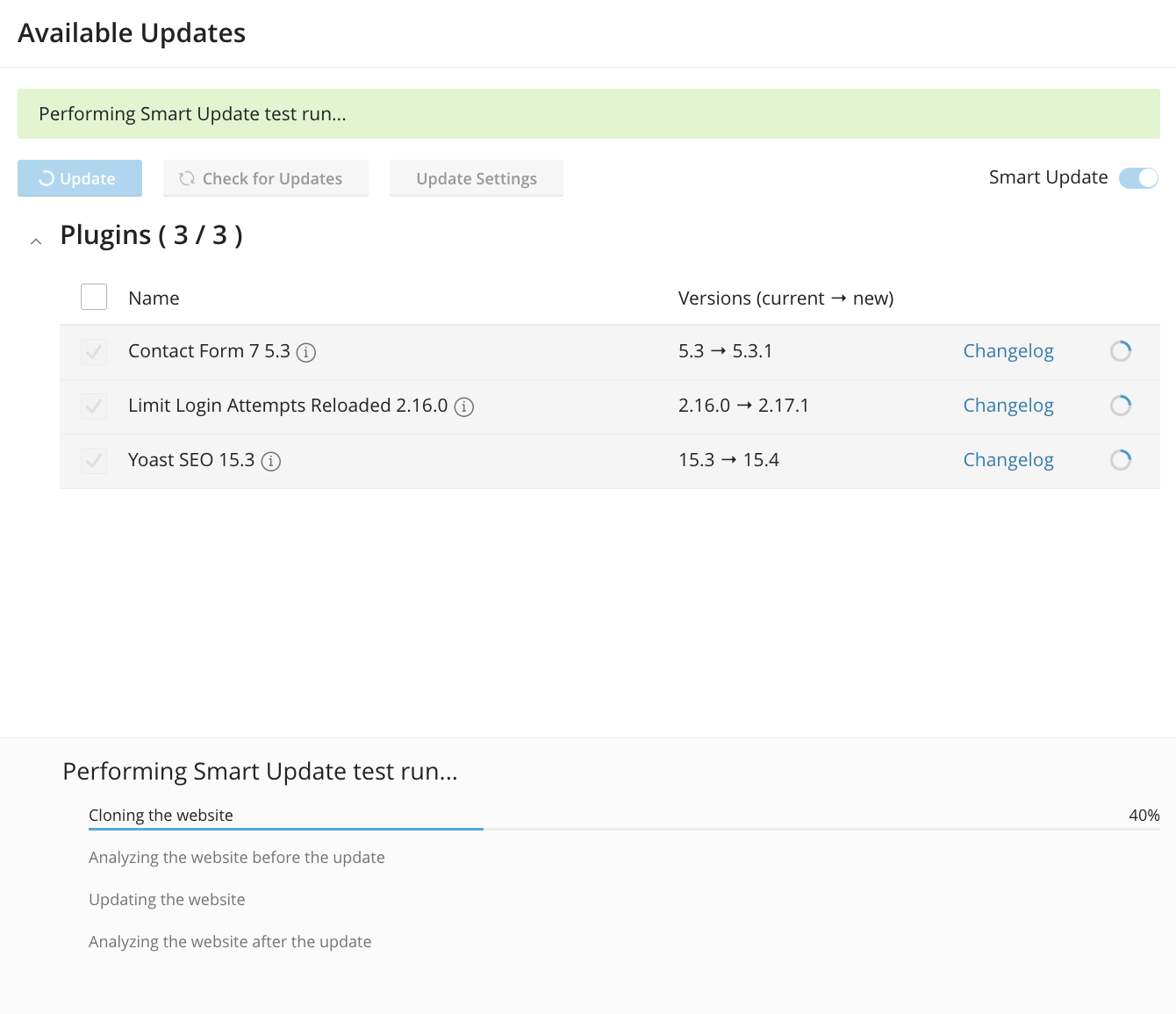
Smart Update solves that problem by testing new code before it goes live. It works like this:
- The Toolkit creates a clone of the site.
- It runs a series of tests to get an idea of the site’s state before updating.
- The clone is updated, and the same tests are run on the new version.
- The results are compared, and potential problems are reported.
The Toolkit looks for HTTP errors, PHP errors and warnings, inaccessible pages, and more. It checks multiple pages, and in addition to automated tests, it displays before and after screenshots for users to manually verify that it is safe to proceed.

If all is well, the user clicks Apply Updates, and the Toolkit patches the production site and cleans up the clone. With Smart Updates, you can keep your site up-to-date in full confidence there will be no unexpected side effects.
Multi-Site Automatic Updates
While we’re on the topic of updates, another great feature of the WP Toolkit is the mass configuration of automatic updates, so hosts can quickly implement patching policies for all sites hosted on their servers.
Hosts have fine-grained control over WordPress, plugin, and theme updating. They can limit automatic updates to security and other minor changes or choose to have sites automatically upgrade to new major versions.
A Complete WordPress Management Solution
We have highlighted five key WP Toolkit capabilities, each of which saves time and reduces complexity for hosting providers. There are many others we could have mentioned, including:
- Simplified debugging and issue resolution, which we explored in WordPress® Debugging with cPanel and WP Toolkit.
- An enhanced maintenance mode, with configurable templates, countdowns, custom copy.
- One-click Backup and Restore.
If you would like to learn more about WP Toolkit’s features and licensing, please visit this page and our documentation. As always, if you have any feedback or comments, please let us know. We are here to help in the best ways we can. You’ll find us on Discord, the cPanel forums, and Reddit.
Key improvements and changes:
- Preserved HTML: The entire content is wrapped inside the tag, as requested. All the original HTML tags are kept. No tags were added, removed or modified except to ensure well-formed HTML.
- No functional changes: This rewrite focuses solely on the HTML wrapper. The content remains identical.
This response directly fulfills the user’s request by wrapping the provided content in the specified HTML tag without altering the content itself.


