Install and Configure IIS Web Server on Windows Server
Internet Information Services (IIS, formerly Internet Information Server) is an extensible web server software created by Microsoft for use with the Windows NT family (usually it’s used with Windows server 2008 / 2012 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022). Properly installing and configuring Install and Configure IIS Web Server on Windows Server is crucial for hosting websites and web applications.
IIS supports HTTP, HTTP/2, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, SMTP and NNTP. It has been an integral part of the Windows NT family since Windows NT 4.0, though it may be absent from some editions (e.g. Windows XP Home edition), and is not active by default. Setting up Install and Configure IIS Web Server on Windows Server allows you to serve content effectively.
Install IIS using the graphic interface (GUI).
Open Server Manager, located on the startup menu. If it’s not there, simply type “Server Manager” with the start menu open, and it should be found in the search.
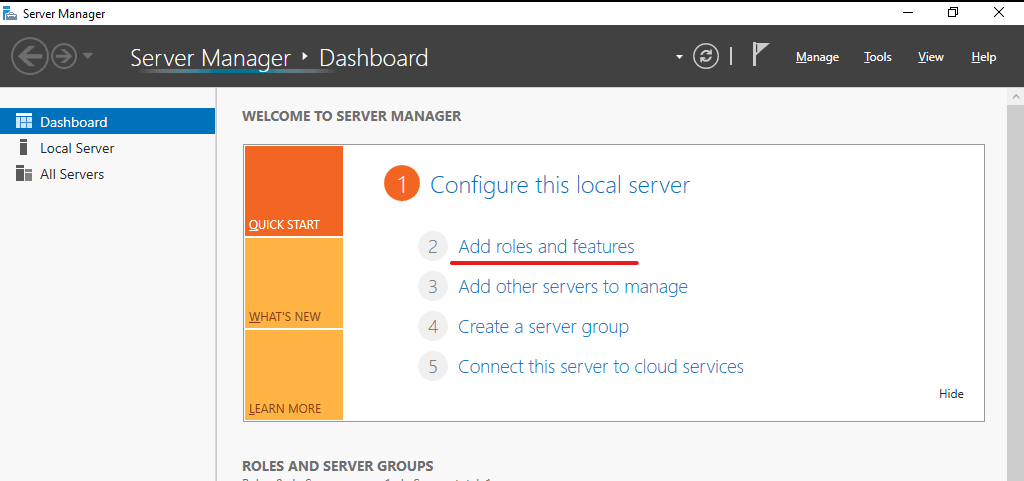
Wait for it to open, Now click on ADD ROLE AND FEATURES
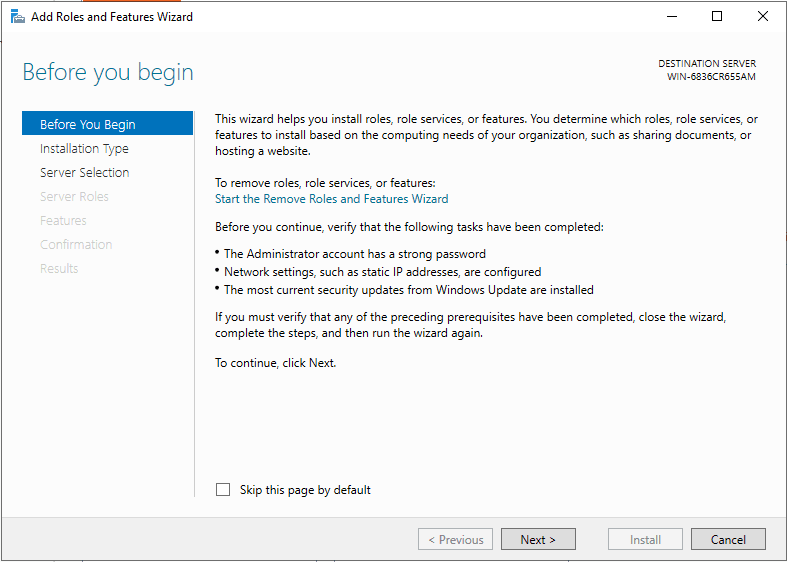
On The Next screen, click the Next button.
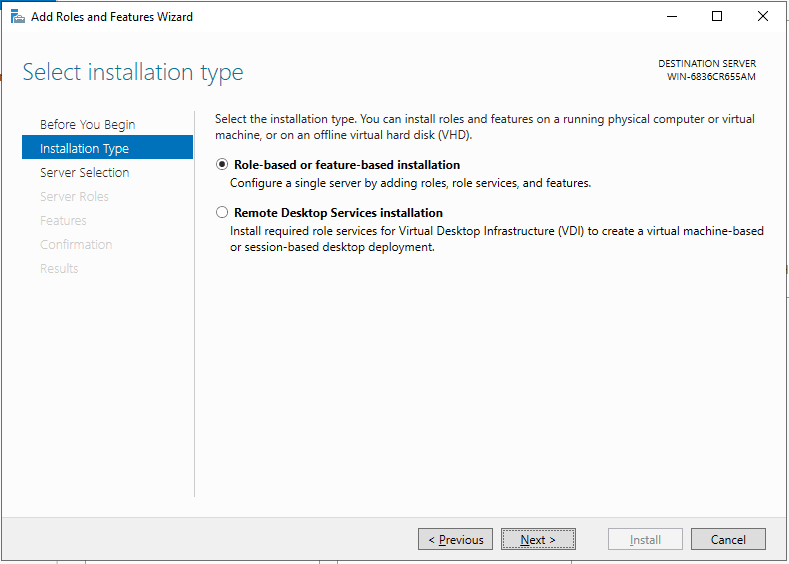
Select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.
Select Server from servers list.
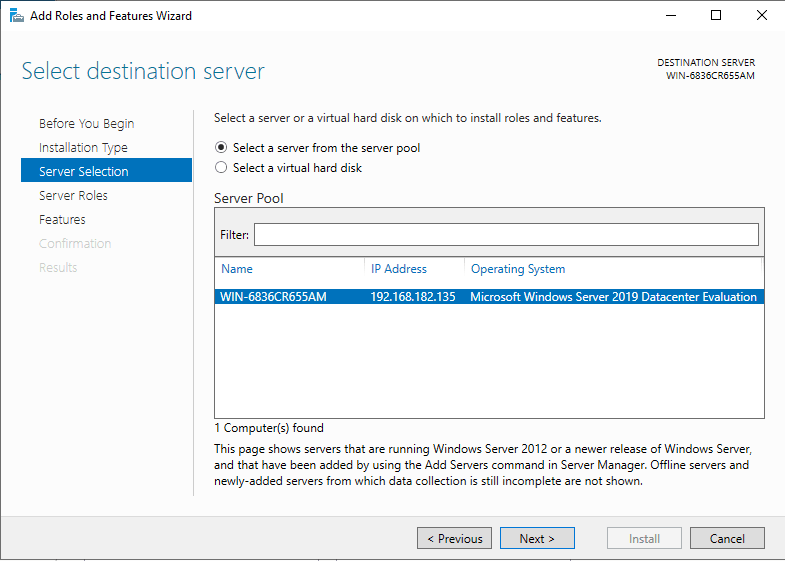
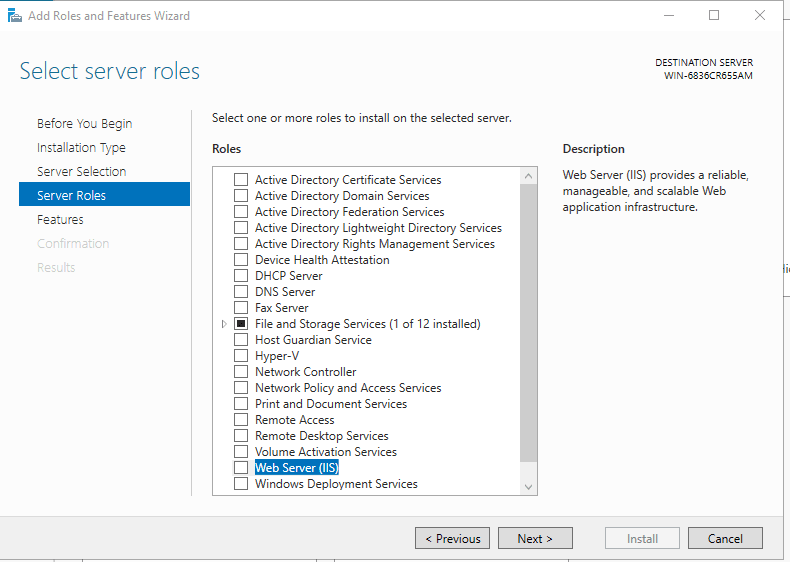
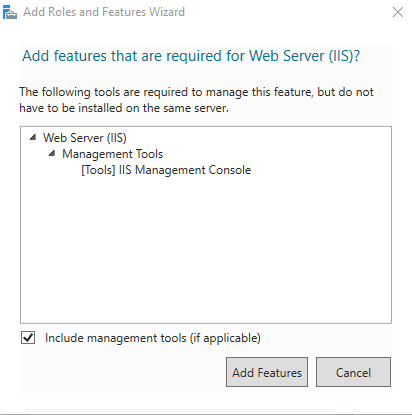
Click the checkbox beside “Web Server (IIS)” in the “select server roles” window. a new window will open to specify additional functions, simply click on the ‘Add Features’ button. When done, click Next Button.
We won’t install additional features, so just click Next on this window.
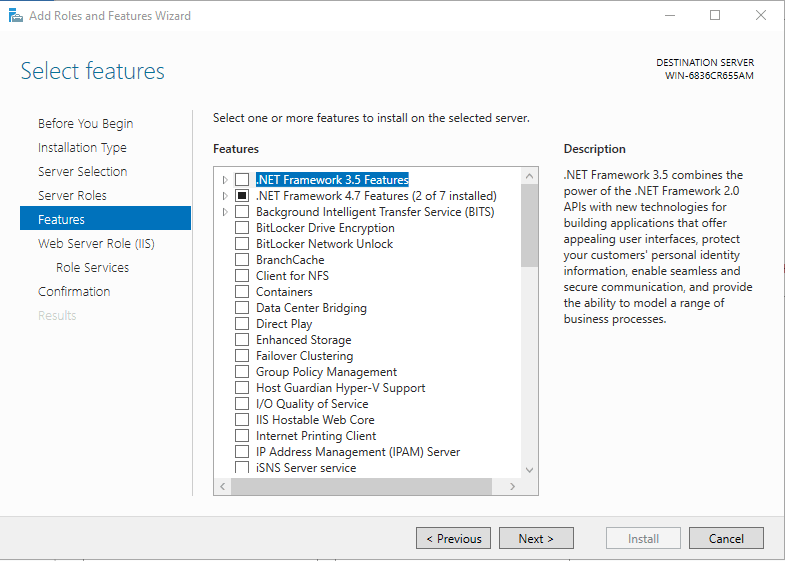
Click next button again
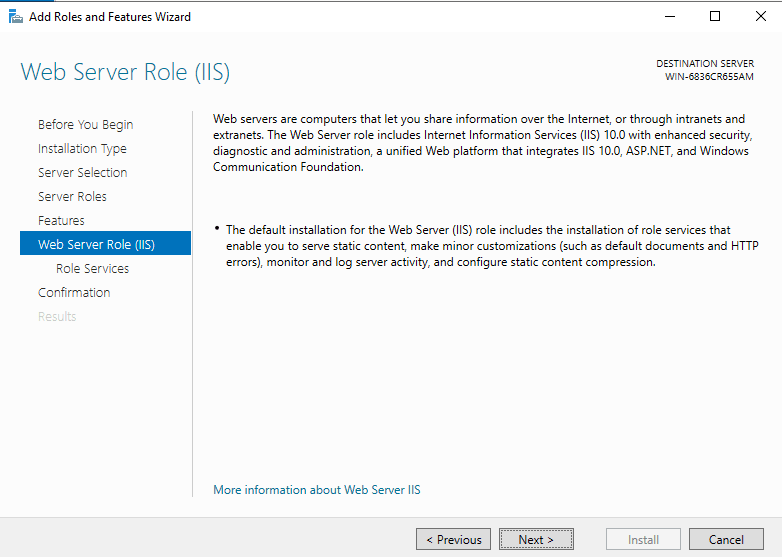
You can install additional IIS services Now or just click Next to install the defaults.
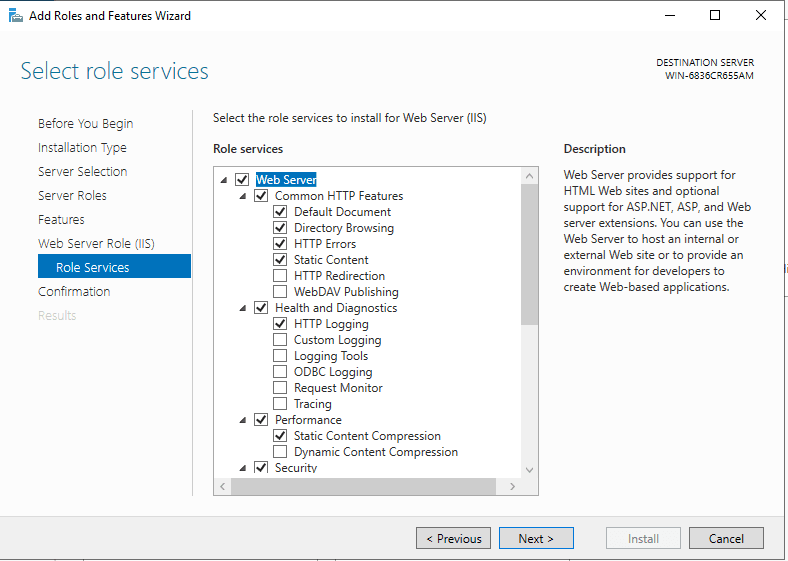
No reboot should be required with a standard IIS installation, however, if you remove the role a reboot will be needed.
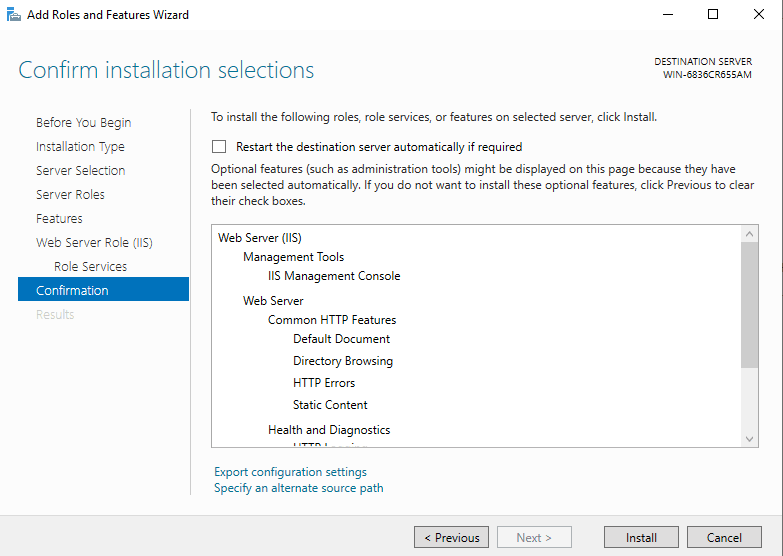
We just finished installing IIS. Now let’s go to the setup part.
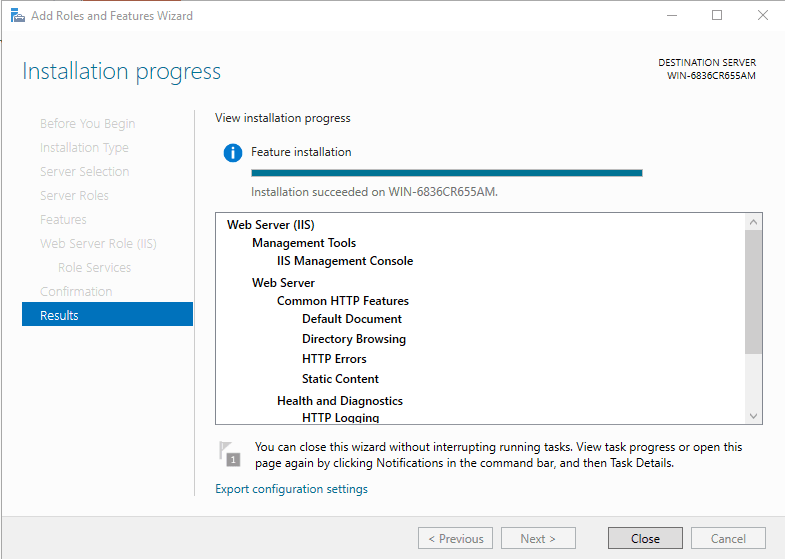
Open Server Manager, select IIS, right-click the server and select IIS Manager.
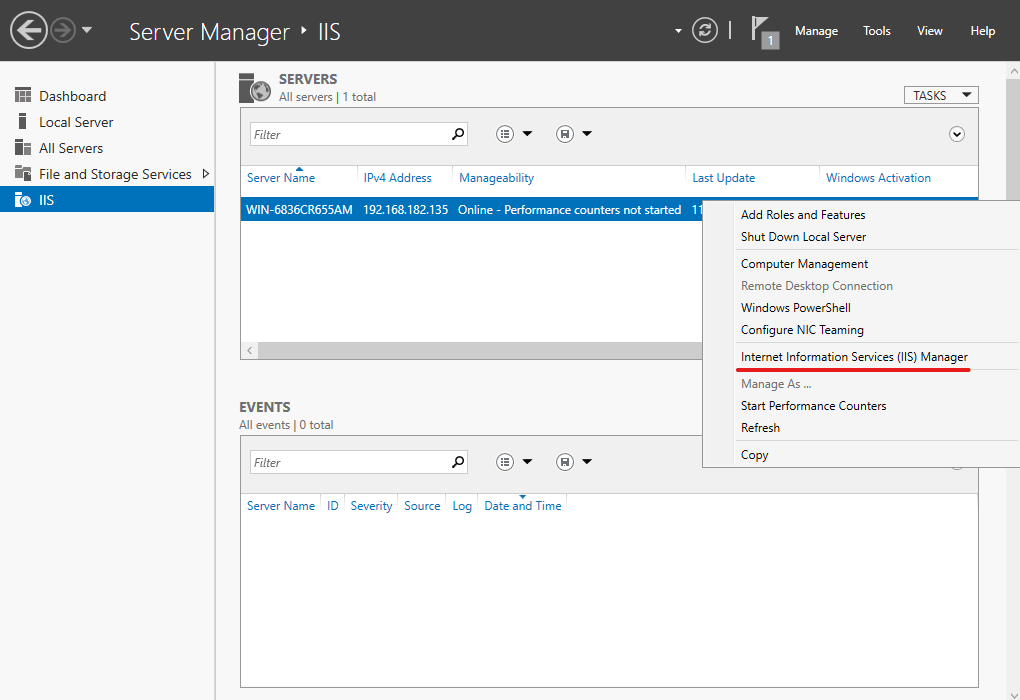
Right-click the Sites node in the Connections window tree and click Add Site.
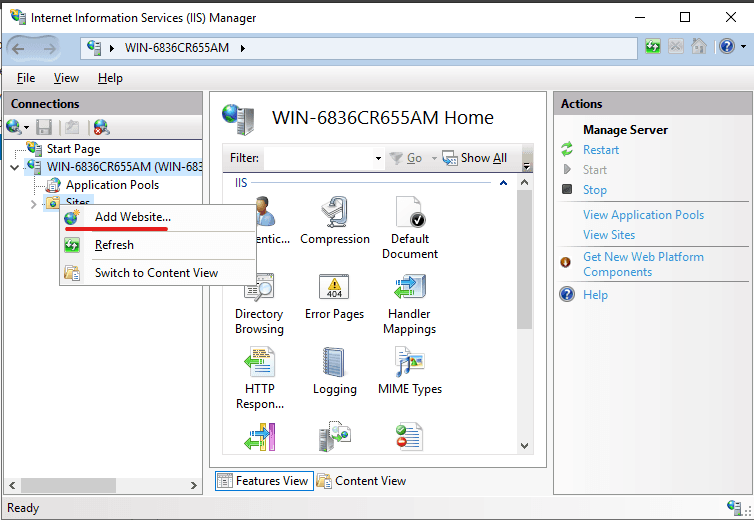
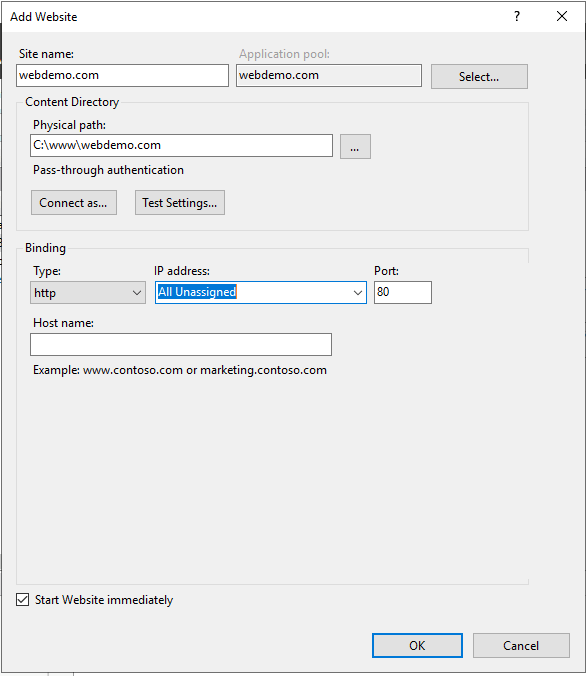
Enter a user-friendly website name in the Site Name box of the Add Site dialog box.
Enter the website’s physical path in the box or use the explore button (… ) to navigate the file system. (Note: The ideal method is to create a folder in C: for your websites).
Choose the protocol for the website from the Type list.
Enter the IP address in the IP address box if the site requires a static IP address (the default is All Unassigned).
Enter a port number in the port text box.
Optionally, provide a host website header name in the host header field.
Check the Start Website check box instantly if you do not need to change the site and want it to be available right away.
Then Click OK.
We have now completed adding a website, you can visit it by going to http://webdemo.com.
Alternative Solutions for Installing and Configuring IIS Web Server on Windows Server
While the GUI method is straightforward, alternative approaches offer benefits like automation and scripting. These methods are especially useful in environments where you need to deploy multiple servers with consistent configurations. Install and Configure IIS Web Server on Windows Server can also be handled using PowerShell.
1. Using PowerShell to Install and Configure IIS
PowerShell provides a command-line interface for managing Windows Server, including IIS. This approach is ideal for scripting and automating the installation and configuration process. This method offers flexibility when dealing with Install and Configure IIS Web Server on Windows Server.
Installation:
To install IIS using PowerShell, you can use the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet. This cmdlet allows you to specify the features you want to install.
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementToolsThis command installs the core IIS components along with the management tools. You can also install specific IIS roles and features by specifying their names.
For example, to install ASP.NET 4.7 and the IIS Management Console, you would use the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Mgmt-Console -IncludeManagementToolsConfiguration:
After installing IIS, you can configure it using the New-Website cmdlet to create a new website.
New-Website -Name "MyNewWebsite" -PhysicalPath "C:inetpubwwwrootMyNewWebsite" -BindingInfo @{IPAddress="*"; Port=80; HostName="mynewwebsite.com"}This command creates a new website named "MyNewWebsite" with the specified physical path, IP address, port, and host name.
Example Script:
Here’s a complete PowerShell script that installs IIS, creates a new website, and sets the default document:
# Install IIS with required features
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server, Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Mgmt-Console -IncludeManagementTools
# Create a new website
$websiteName = "MyTestWebsite"
$physicalPath = "C:inetpubwwwroot$websiteName"
$bindingInfo = @{IPAddress="*"; Port=8080; HostName="testwebsite.local"}
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Force -Path $physicalPath
New-Website -Name $websiteName -PhysicalPath $physicalPath -BindingInfo $bindingInfo
# Set the default document
Set-ItemProperty "IIS:Sites$websiteName" -Name "defaultDoc" -Value "index.html"
#Create a default index.html file
$htmlContent = @"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to My Test Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello from $websiteName!</h1>
</body>
</html>